BECE 2001 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The main pollutant from domestic fires is
Solution: Carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion in domestic fires and is a toxic gas that poses significant health risks.
2. Plantain is propagated vegetatively by
Solution: Plantain reproduces through suckers, which are shoots emerging from the base of the parent plant and developing into independent plants.
3. Which of the following gases supports combustion?
Solution: Oxygen is essential for combustion as it acts as an oxidizing agent in chemical reactions involving burning.
4. The main function of petals in a flower is to
Solution: Petals attract pollinators like insects through bright colors and scents, facilitating cross-pollination.
5. The organ in the human body which is responsible for the removal of urea is the
Solution: Kidneys filter blood to remove urea and other nitrogenous wastes, excreting them as urine.
6. The sun and the planets form the
Solution: The solar system comprises the sun and celestial bodies (planets, moons, etc.) bound by its gravity.
7. The bilharzia worm can enter the human body through the
Solution: Bilharzia larvae penetrate human skin during contact with contaminated water, causing infection.
8. Brass is an alloy of copper and
Solution: Brass is a durable alloy primarily composed of copper (∼70%) and zinc (∼30%), used in fittings and instruments.
9. Which of the following diseases is contracted through infected wounds?
Solution: Tetanus spores (e.g., from soil) enter through wounds, producing toxins that cause muscle rigidity.
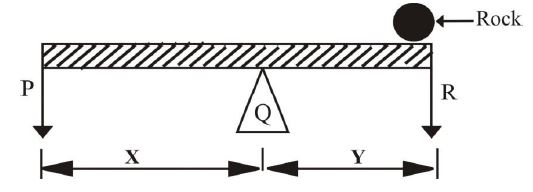
Use the figure below to answer Questions 10 and 11
A rigid bar is balanced horizontally at a point by placing a rock on the bar as shown
10. Which of the parts labeled represents the pivot?
Solution: The pivot (fulcrum) is the fixed point (Q) where the bar rotates, enabling balance.
11. The effort is represented by
Solution: Effort (P) is the applied force to lift the load, acting at one end of the lever.
12. Which of the following parts of the human body are sense organs?
I. Tongue
II. Hair
III. Nose
IV. Skin
Solution: Tongue (taste), nose (smell), and skin (touch) are sense organs; hair lacks sensory receptors.
13. The function of the cotyledon is to
Solution: Cotyledons store nutrients (e.g., starch, proteins) to nourish the developing seedling during germination.
14. Which of the following substances are components of a fertile soil?
Solution: Fertile soil requires macronutrients like nitrogen (growth), phosphorus (energy transfer), calcium (cell walls), and sulfur (protein synthesis).
15. Which of the following appliances transform(s) electrical energy to heat energy?
I. Swish oven
II. Hair dryer
III. Refrigerator motor
Solution: Ovens and hair dryers convert electricity to heat via resistors; refrigerators use motors for cooling, not heating.
16. A ray of light makes an angle of \( 20^\circ \) with the surface of a plane mirror. Determine the angle of reflection.
Solution: The angle of incidence equals reflection. If light makes \( 20^\circ \) with the surface, it makes \( 70^\circ \) with the normal, so reflection is \( 70^\circ \).
17. Seasonal changes are the result of the
Solution: Earth’s tilt (23.5°) and revolution around the sun cause varying solar intensity, creating seasons.
18. Crystals of sugar were obtained when a hot solution of sugar was cooled to room temperature. What conclusion can be drawn from this observation?
Solution: Cooling a saturated hot solution reduces solubility, causing excess solute (sugar) to crystallize.
19. Which of the following processes about all living things is / are true?
I. Reproduction
II. Respiration
III. Locomotion
IV. Excretion
Solution: All living things reproduce, respire (release energy), and excrete (remove wastes); not all move (e.g., plants).
20. Tendrils in plants are adaptations that enable the plant to
Solution: Tendrils (modified stems/leaves) coil around supports, helping climbing plants access sunlight.
21. The density of a substance is 2.5gcm\(^3\). Calculate the volume of the substance if its mass is 25.0 g.
Solution: Volume = mass / density = 25.0 g / 2.5 g/cm³ = 10.0 cm³.
22. The food substance that promotes good health is
Solution: Vitamins (e.g., C, D) are essential micronutrients that support immunity, growth, and disease prevention.
23. The energy that causes the turbine of hydro-electric plant to rotate is
Solution: Flowing water’s kinetic energy spins turbines, converting motion to mechanical energy for electricity.
24. Which of the following pairs of organs are parts of the central nervous system?
Solution: The central nervous system (CNS) comprises the brain (command center) and spinal cord (signal pathway).
25. Plants manufacture their food using
I. carbon dioxide
II. oxygen
III. light
IV. chlorophyll
Solution: Photosynthesis requires CO₂, light, and chlorophyll to produce glucose; oxygen is a byproduct.
26. Which of the following crops improves soil fertility when cultivated continuously on the same piece of land?
Solution: Peas (legumes) host nitrogen-fixing bacteria in root nodules, enriching soil with nitrogen.
27. It is necessary to keep household refuse in covered containers in order to prevent
Solution: Covered containers block flies (disease vectors) from breeding in or contaminating waste.
28. The fraction of the earth’s surface that faces the sun at any particular time is
Solution: At any instant, half of Earth is illuminated by sunlight (daytime), while the other half is in darkness.
29. Which of the following is a micro-organism?
Solution: Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled organisms; others are visible invertebrates.
30. Which of the following statements about machines is/are correct?
I. Machines help us to do work more easily
II. A force applied at one point of the machine overcomes a load at another point
III. All machines have engines
Solution: Machines simplify work (I) by transmitting force (II); not all have engines (e.g., levers, pulleys).
31. The female part of a flower is called the
Solution: The style is part of the pistil (female structure), connecting the stigma to the ovary.
32. Which of the following substances is a compound?
Solution: Water (H₂O) is a compound of hydrogen and oxygen; others are elements.
33. A solution in which no more solute will dissolve at a particular temperature is said to be
Solution: A saturated solution holds the maximum solute at a given temperature; excess remains undissolved.
34. The process of respiration could be represented by the following equation: Glucose + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide + X . What does X represent?
Solution: Cellular respiration releases energy stored as heat (X), alongside water and CO₂.
35. When oil and water are shaken together they form a mixture called
Solution: Emulsions form when immiscible liquids (e.g., oil, water) mix temporarily via agitation.
36. The organism which lives in the human blood as a parasite is
Solution: Plasmodium (malaria parasite) infects red blood cells during its lifecycle.
37. The fusion of an egg cell with sperm forms
Solution: A zygote is the diploid cell resulting from fertilization, initiating embryonic development.
38. The instrument used to measure current in an electric circuit is the
Solution: Ammeters measure electric current (amperes) and are connected in series in circuits.
39. The atom of an element has 4 protons and 5 neutrons in its nucleus. How many shells are occupied in the atom?
Solution: Atomic number = 4 (beryllium); electron configuration (2,2) occupies two shells (K and L).
40. The gaps left between railway lines is to allow for
Solution: Gaps accommodate thermal expansion of rails on hot days, preventing buckling.
1. QUESTION 1
1. (a) (i) What is surface tension?
(ii) Name two household devices that make use of surface tension
(iii) Explain how the principle of surface tension operates in one of the devices you have named
(b) (i) What is constipation?
(ii) State four ways by which constipation can be prevented
(c) A block of mass 10kg is suspended from a spring. Calculate the force acting on the block. [g = 10ms⁻²]
(d) An amount of sodium hydroxide solution was put into a beaker and a piece of litmus paper was added. Dilute hydrochloric acid was added a little at a time with stirring until the litmus paper just turned purple. The resulting solution was evaporated to dryness.
(i) What was the colour of the litmus paper in the sodium hydroxide solution?
(ii) What does the colour change of the litmus paper indicate?
(iii) What substance was left after the evaporation?
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the reaction that took place.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a)
(i) Surface tension is the condition existing at the surface of a liquid, resembling a stretched elastic skin.
OR
The property of a liquid that makes its surface behave like a stretched elastic skin.
(ii) Household devices: Umbrella, raincoat, tents (any two).
(iii) Explanation: The cohesive forces among water molecules cause water to behave like a stretched elastic skin over the pores of devices (e.g., umbrella), preventing water penetration.
(b)
(i) Constipation is a condition where elimination of solid waste is difficult, with hard/dry feces.
(ii) Prevention methods:
- Drink plenty of water/liquids
- Eat fruits/vegetables regularly
- Consume high-fiber foods (e.g., wheat, barley)
- Get adequate sleep
- Exercise regularly
(c) Force = mass × gravity = 10 kg × 10 ms⁻² = 100 N
(d)
(i) Blue
(ii) Indicates neutralization is complete / solution changed from basic to neutral.
(iii) Sodium chloride (common salt)
(iv) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O
2. QUESTION 2
2. (a) State and explain three ways by which plants protect themselves from danger
(b) (i) What is an anion?
(ii) Give the names of the products formed when the following pairs of compounds react together:
(a) NH₄OH and dilute HCl
(β) CaCO₃ and dilute HCl
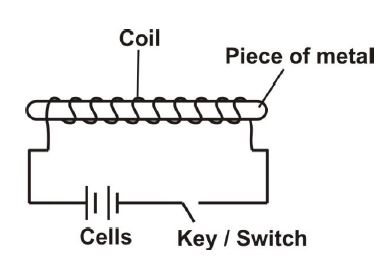
(c) (i) What is electromagnetism?
(ii) With the aid of a circuit diagram describe how a piece of metal can be magnetized
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a) Protection methods (any three):
- Unpleasant smell repels animals
- Unpleasant taste deters consumption
- Sharp thorns/spines prevent touch
- Poisonous parts cause irritation/death
- Sticky secretions cause discomfort
(b)
(i) Anion: A negatively charged atom / atom that gained electrons.
(ii) Products:
(a) Ammonium chloride and water
(β) Calcium chloride, carbon dioxide, and water
(c)
(i) Electromagnetism: Magnetism produced by electric current.
(ii) Magnetization process:
- Connect metal to DC source via coil
- Current flow creates magnetic field
- Metal retains magnetism after current stops
3. QUESTION 3
3. (a) State (i) three characteristics of roots
(ii) two functions of roots
(b) State two conditions necessary for the germination of seeds
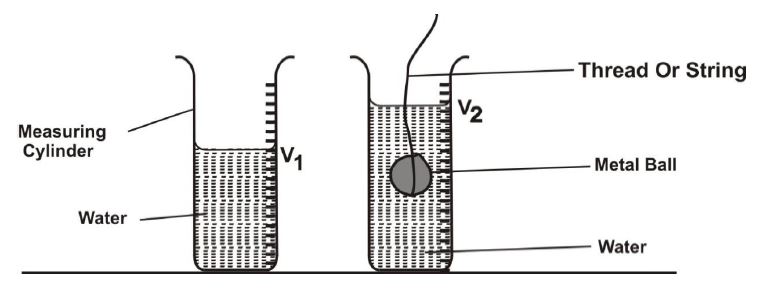
(c) Describe briefly how the volume of an irregular shaped metal ball could be determined
(d) Write down the chemical formula for each of the following compounds:
(i) sodium chloride
(ii) copper sulphate
(iii) magnesium sulphate
(iv) potassium carbonate
(e) State the method that could be used to separate each of the following compounds:
(i) iodine and sand
(ii) ethanol and water
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a)
(i) Root characteristics (any three):
- Grow underground
- Grow downward
- Grow away from light
- Develop from radicle
- Cream/brown color
- Have root hairs
(ii) Root functions:
- Absorb water/minerals
- Anchor plant
- Store food
(b) Germination conditions:
- Seed viability
- Suitable temperature
- Water/moisture
- Air/oxygen
(c) Volume determination:
- Fill measuring cylinder with water (record V₁)
- Submerge metal ball (record V₂)
- Volume = V₂ - V₁
(d) Chemical formulas:
(i) NaCl
(ii) CuSO₄
(iii) MgSO₄
(iv) K₂CO₃
(e) Separation methods:
(i) Sublimation
(ii) Distillation
4. QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) What is digestion?
(ii) Describe briefly how food is digested in the stomach
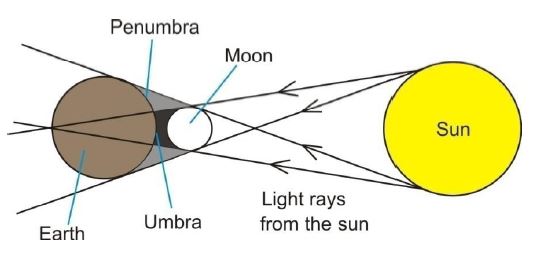
(b) (i) What is meant by eclipse of the sun?
(ii) With the aid of a labelled diagram, distinguish between total eclipse and partial eclipse
(c) (i) State the difference between a physical change and a chemical change
(ii) Give one example of each of a physical change and a chemical change
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4. (a)
(i) Digestion: Breakdown of food into absorbable simpler forms.
(ii) Stomach digestion:
- Protein digestion begins
- Gastric juice (HCl + enzymes) secreted
- HCl creates acidic medium
- Enzymes break proteins
(b)
(i) Solar eclipse: Moon blocks Sun's light from reaching Earth.
(ii) Diagram distinction:
- Total eclipse: Moon completely covers Sun (umbra region)
- Partial eclipse: Moon partially covers Sun (penumbra region)
(c)
(i) Differences:
Physical change: No new substance, reversible
Chemical change: New substance, irreversible
(ii) Examples:
Physical: Melting ice
Chemical: Rusting iron